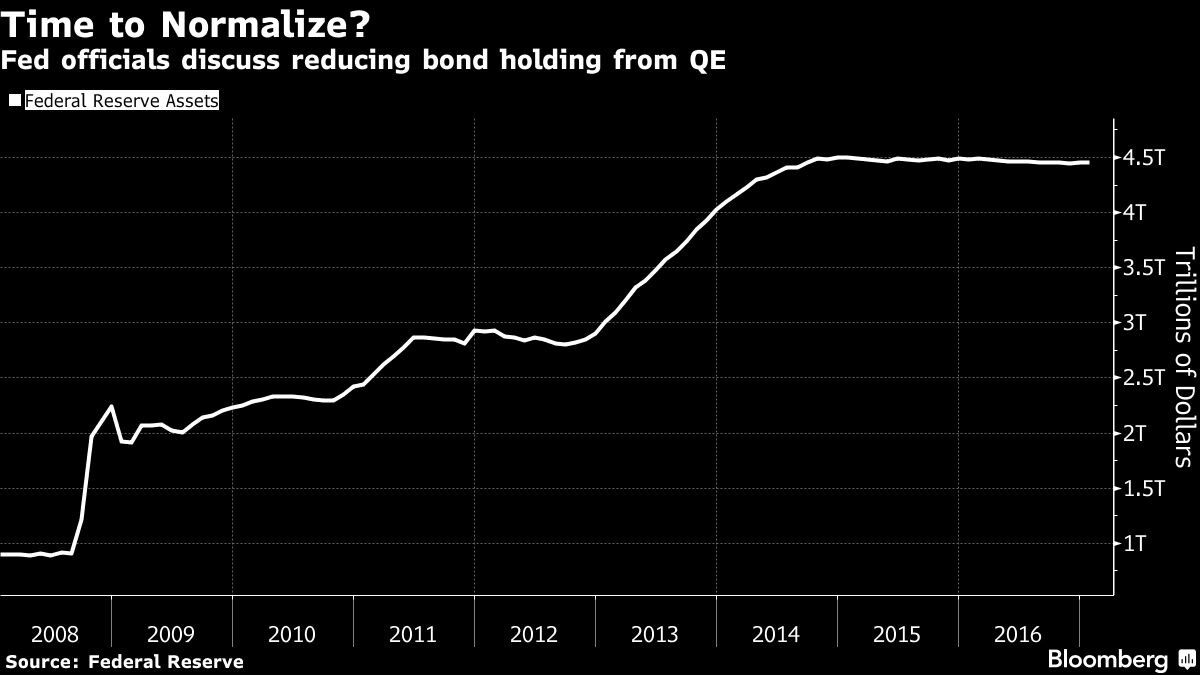
Almost a decade after it all began, the Federal Reserve is finally talking about unwinding its grand experiment in monetary policy.
And when it happens, the knock-on effects in the bond market could pose a threat to the U.S. housing recovery.
Just how big is hard to quantify. But over the past month, a number of Fed officials have openly discussed the need for the central bank to reduce its bond holdings, which it amassed as part of its unprecedented quantitative easing during and after the financial crisis. The talk has prompted some on Wall Street to suggest the Fed will start its drawdown as soon as this year, which has refocused attention on its $1.75 trillion stash of mortgage-backed securities.
Almost a decade after it all began, the Federal Reserve is finally talking about unwinding its grand experiment in monetary policy.
And when it happens, the knock-on effects in the bond market could pose a threat to the U.S. housing recovery.
Just how big is hard to quantify. But over the past month, a number of Fed officials have openly discussed the need for the central bank to reduce its bond holdings, which it amassed as part of its unprecedented quantitative easing during and after the financial crisis. The talk has prompted some on Wall Street to suggest the Fed will start its drawdown as soon as this year, which has refocused attention on its $1.75 trillion stash of mortgage-backed securities.
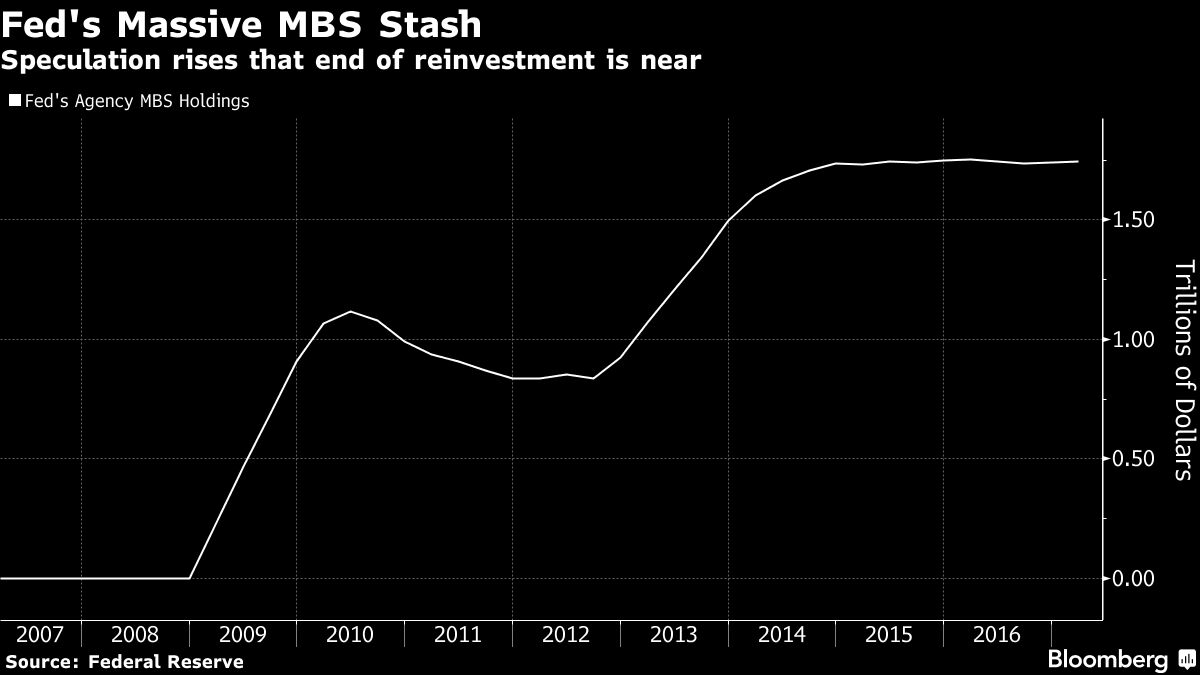
While the Fed also owns Treasuries as part of its $4.45 trillion of assets, its MBS holdings have long been a contentious issue, with some lawmakers criticizing the investments as beyond what’s needed to achieve the central bank’s mandate. Yet because the Fed is now the biggest source of demand for U.S. government-backed mortgage debt and owns a third of the market, any move is likely to boost costs for home buyers.
In the past year alone, the Fed bought $387 billion of mortgage bonds just to maintain its holdings. Getting out of the bond-buying business as the economy strengthens could help lift 30-year mortgage rates past 6 percent within three years, according to Moody’s Analytics Inc.
Unwinding QE “will be a massive and long-lasting hit” for the mortgage market, said Michael Cloherty, the head of U.S. interest-rate strategy at RBC Capital Markets. He expects the Fed to start paring its investments in the fourth quarter and ultimately dispose of all its MBS holdings.
Unprecedented Buying
Unlike Treasuries, the Fed rarely owned mortgage-backed securities before the financial crisis. Over the years, its purchases have been key in getting the housing market back on its feet. Along with near-zero interest rates, the demand from the Fed reduced the cost of mortgage debt relative to Treasuries and encouraged banks to extend more loans to consumers.
In a roughly two-year span that ended in 2014, the Fed increased its MBS holdings by about $1 trillion, which it has maintained by reinvesting its maturing debt. Since then, 30-year bonds composed of Fannie Mae-backed mortgages have only been about a percentage point higher than the average yield for five- and 10-year Treasuries, data compiled by Bloomberg show. That’s less than the spread during housing boom in 2005 and 2006.
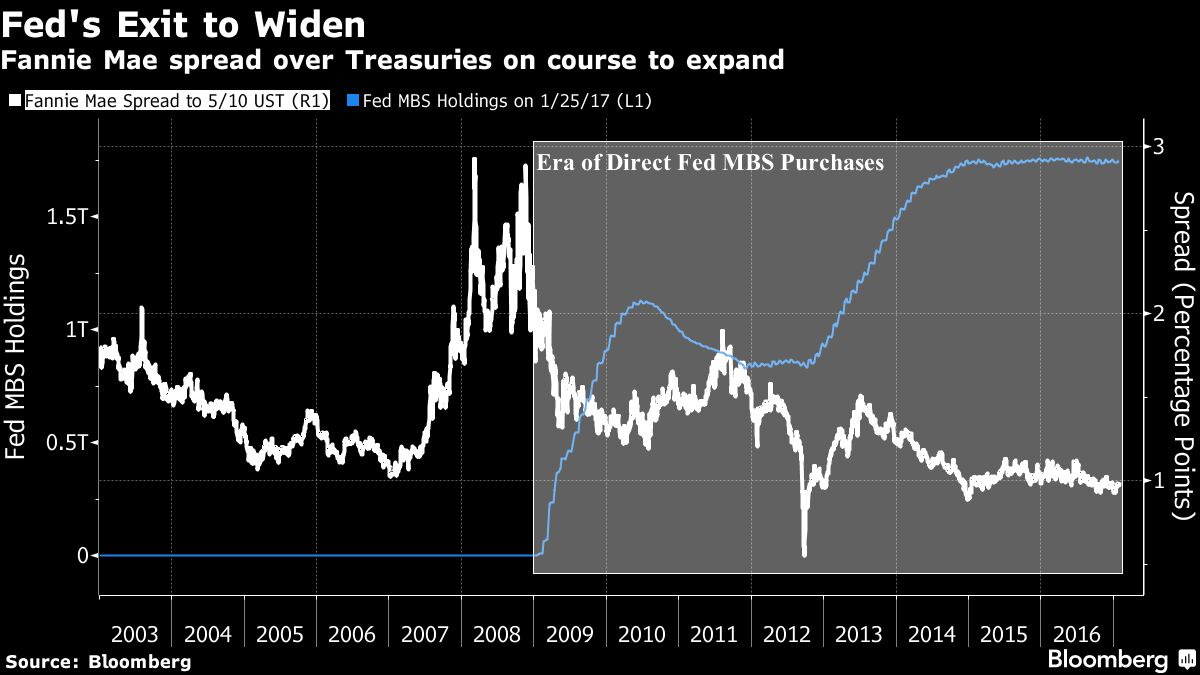
Talk of the Fed pulling back from the market has bond dealers anticipating that spreads will widen. Goldman Sachs Group Inc. sees the gap increasing 0.1 percentage point this year, while strategists from JPMorgan Chase & Co. say that once the Fed actually starts to slow its MBS reinvestments, the spread would widen at least 0.2 to 0.25 percentage points.
“The biggest buyer is leaving the market, so there will be less demand for MBS,” said Marty Young, fixed-income analyst at Goldman Sachs. The firm forecasts the central bank will start reducing its holdings in 2018. That’s in line with a majority of bond dealers in the New York Fed’s December survey.
The Fed, for its part, has said it will keep reinvesting until its tightening cycle is “well underway,” according to language that has appeared in every policy statement since December 2015. The range for its target rate currently stands at 0.5 percent to 0.75 percent.
Mortgage Rates
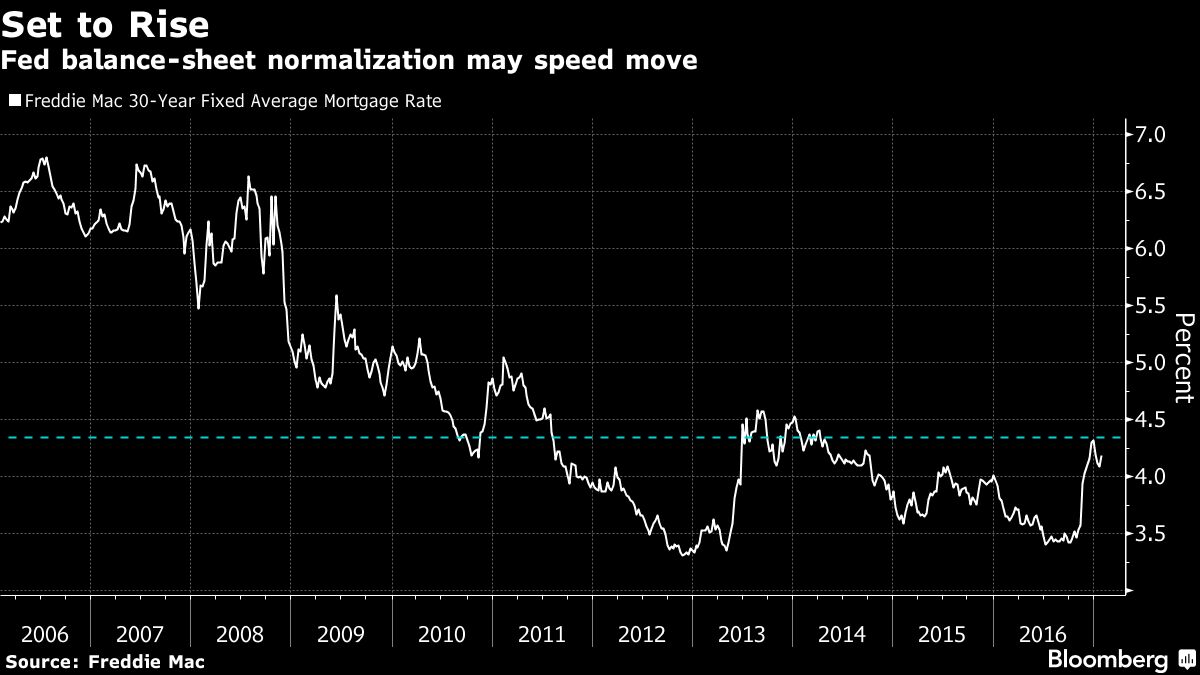
Mortgage rates have started to rise as the Fed moves to increase short-term borrowing costs. Rates for 30-year home loans surged to an almost three-year high of 4.32 percent in December. While rates have edged lower since, they’ve jumped more than three-quarters of a percentage point in just four months.
The surge in mortgage rates is already putting a dent in housing demand. Sales of previously owned homes declined more than forecast in December, even as full-year figures were the strongest in a decade, according to data from the National Association of Realtors.
People are starting to ask the question, “Gee, did I miss my opportunity here to get a low-rate mortgage?” said Tim Steffen, a financial planner at Robert W. Baird & Co. in Milwaukee. “I tell them that rates are still pretty low. But are rates going to go up? It certainly seems like they are.”
Part of it, of course, has to do with the Fed simply raising interest rates as inflation perks up. Officials have long wanted to get benchmark borrowing costs off rock-bottom levels (another legacy of crisis-era policies) and back to levels more consist with a healthy economy. This year, the Fed has penciled in three additional quarter-point rate increases. Traders, meanwhile, have priced in slightly less than two increases in 2017.
The move to taper its investments has the potential to cause further tightening. Morgan Stanley estimates that a $325 billion reduction in the Fed’s MBS holdings from April 2018 through end of 2019 may have the same impact as nearly two additional rate increases.
Finding other sources of demand won’t be easy either. Because of the Fed’s outsize role in the MBS market since the crisis, the vast majority of transactions are done by just a handful of dealers. What’s more, it’s not clear whether investors like foreign central banks and commercial banks can absorb all the extra supply -- at least without wider spreads.
On the plus side, getting MBS back into the hands of private investors could help make the market more robust by increasing trading. Average daily volume has plunged more than 40 percent since the crisis, Securities Industry and Financial Markets Association data show.
“Ending reinvestment will mean there are more bonds for the private sector to buy,” said Daniel Hyman, the co-head of the agency-mortgage portfolio management team at Pacific Investment Management Co.
What’s more, it may give the central bank more flexibility to tighten policy, especially if President Donald Trump’s spending plans stir more economic growth and inflation. St. Louis Fed President James Bullard said last month that he’d prefer to use the central bank’s holdings to do some of the lifting, echoing remarks by his Boston colleague Eric Rosengren.
Nevertheless, the consequences for the U.S. housing market can’t be ignored.
The “Fed has already hiked twice and the market is expecting” more, said Munish Gupta, a manager at Nara Capital, a new hedge fund being started by star mortgage trader Charles Smart. “Tapering is the next logical step.”
No comments:
Post a Comment